
- #Dbschema mongodb design how to#
- #Dbschema mongodb design update#
- #Dbschema mongodb design password#
Navigate to your new database, and you will see a cluster.
#Dbschema mongodb design password#
Finally, create a username and password with read and write permissions, then scroll down and click “Finish and Close.” The shared instance comes with sample datasets you can use for your own applications. Choose the “Shared” or “Free Tier” instance, which is free. You will be prompted to choose a serverless, dedicated or shared database instance. Under “Deployment,” on the Database tab, click “Create.” To get started, you need to sign up for an account at. Here is what you need to follow along with the examples: Let’s get you set up so you can work through the examples in these articles.
#Dbschema mongodb design how to#
In the next article, we will look at how to manage data in MongoDB using CRUD operations. U pdate - Allows you to edit existing entriesĭ elete - Allows you to remove existing entries R ead - Allows you to view or search existing entries CRUD is an acronym that describes actions you can take on your data. In the database world, any data change is performed through CRUD operations.
#Dbschema mongodb design update#
For example, if a user deletes a note in an application’s front end, that operation must be carried out on your back-end server to update the database. To support your application, you’ll likely need to manipulate the data. Understanding the general architecture of Mongo is very helpful, especially when working with large applications where data may be dispersed across different databases but used together to support an application. Many other data types are supported and can be found in the official documentation at MongoDB. You can see that the date field holds a value for a date datatype, the note field holds a string value, the keywords field holds an array of strings and so on. Notice that the data stored in this document contain different data types. The second document contains data stored in the form of field-value pairs. In the example above, we can see that a database called “Notes” contains multiple documents. Let’s take a brief look at how data looks when stored in Mongo: Although Mongo stores data in field-value pairs, it holds many different data types such as strings, integers, arrays, objects, booleans and more!
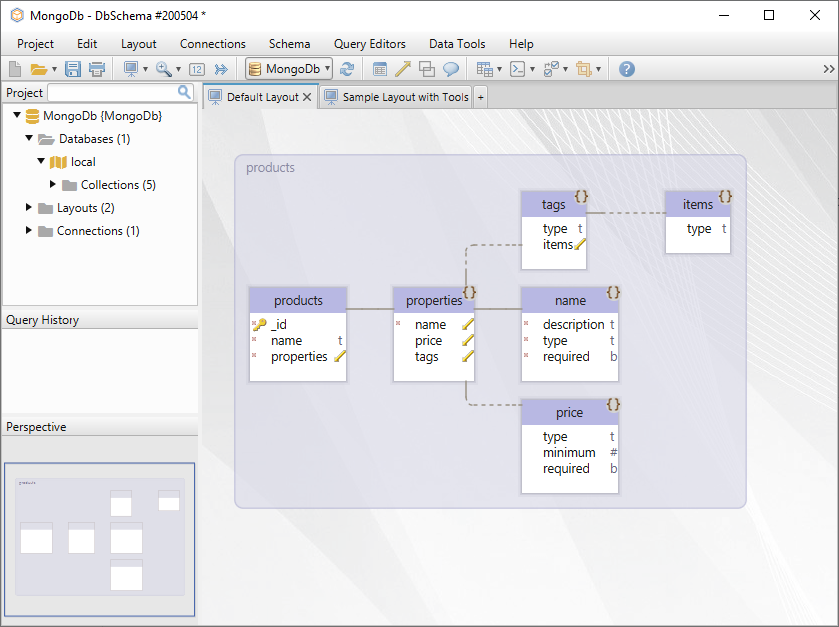
However, no relationship between documents in a collection is required. Collections are used to group documents together for organizational purposes. The value is the data type of this information you wish to store.įor example, you may have a document with a date field holding a string that contains the date the data was stored in the document. The field is a field value that holds data for a data point. Documents hold values for your data in the form of field-value pairs. MongoDB stores data in documents in either JSON, BSON or XML format.

You need to be familiar with four attributes of MongoDB to work successfully with a MongoDB database.
Some major companies using MongoDB to support their mission-critical applications are eBay, Shutterfly and the company behind many popular sports games called Electronic Arts (commonly known as EA Sports). Many prominent companies prefer NoSQL databases to store and manage their applications’ data. On the other hand, NoSQL databases have advantages over relational databases in that they have flexible data models, are easier to implement, support horizontal scaling and offer opportunities for faster queries (, 2022). By the early 2000s, many developers had grown weary of being restricted to the predefined schema that made implementation difficult. SQL databases are also known as relational databases. Why MongoDB?īefore the NoSQL databases, SQL databases reigned supreme. To determine whether MongoDB or another database type is suitable for your application use case, check out the ‘Where to use MongoDb’ whitepaper published by MongoDB. NoSQL databases, such as MongoDB, allow you to facilitate faster querying and make it easy to scale out an organization’s architecture and change the structure of documents stored in your database to suit your application requirements. In addition to document databases, other types of NoSQL databases include graph databases, field-value stores and so on. This database does not use rows, columns and tables to organize data. A NoSQL database is a database that does not use SQL (Structured Query Language). It is a document database that makes it easy for developers to map and store data for their applications. Founded in 2007, MongoDB is a NoSQL database that stores data in JSON, BSON or XML format.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
